HiggsToTauTau analysis: serial
Overview
Teaching: 5 min
Exercises: 20 minQuestions
Challenge: write the HiggsToTauTau analysis workflow and run it on REANA
Objectives
Develop a full HigssToTauTau analysis workflow using a simple serial language
Get acquainted with writing moderately complex REANA examples
Overview
In the previous two episodes we have practised writing and running workflows on REANA using a simple RooFit analysis example.
In this episode we shall go back to the HiggsToTauTau analysis example that you used throughout the workshop and we shall write a serial workflow to run this analysis on the REANA platform.
Recap
In the past two days of this workshop you have followed two lessons:
The lessons were using a HiggsToTauTau example analysis described in detail here:
You have containerised this analysis by means of two GitLab repositories:
gitlab.cern.ch/johndoe/awesome-analysis-eventselectioncontaining the skimming and histogramming;gitlab.cern.ch/johndoe/awesome-analysis-statisticscontaining the statistical modelling and fitting.
You have used the GitLab CI/CD to build the Docker images for these repositories and published them as:
gitlab-registry.cern.ch/johndoe/awesome-analysis-eventselection:master-sha1agitlab-registry.cern.ch/johndoe/awesome-analysis-statistics:master-sha1b
You have run the containerised HiggsToTauTau analysis “manually” by using docker commands for
various analysis steps such as:
bash skim.sh ...bash histograms.sh ...bash plot.sh ...bash fit.sh ...
And you have produced the plots and the fit:
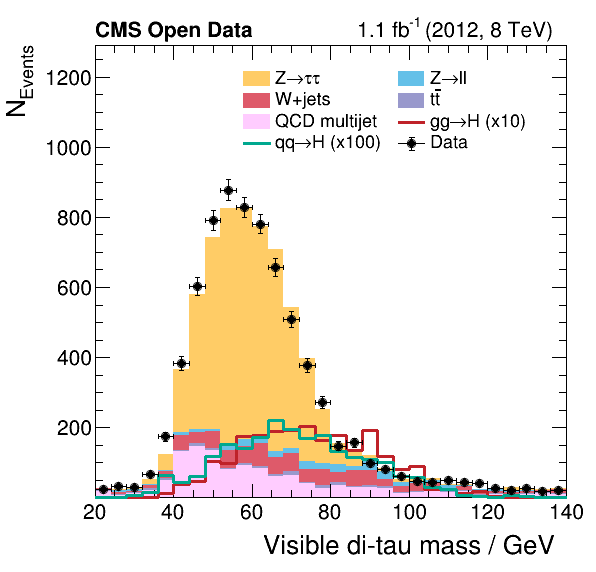
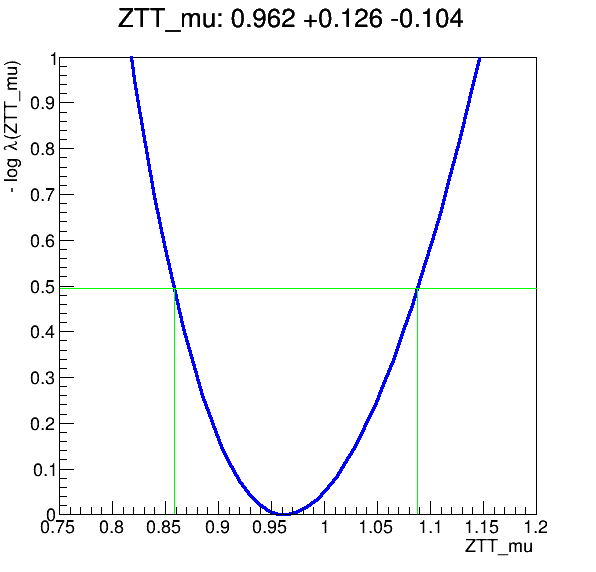
If you haven’t fully followed the previous lessons on Docker and GitLab CI/CD…
Note that if you haven’t fully followed the previous lessons on Docker and GitLab CI/CD and so you haven’t produced your own container images
gitlab.cern.ch/johndoe/awesome-analysis-eventselectionandgitlab.cern.ch/johndoe/awesome-analysis-statistics, you can follow the rest of the episodes in this lesson using the following example imagesgitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3:masterandgitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-statistics-stage3:master. It is these images that we shall use in the solutions to the exercises below.
Objective
Let us write a serial computational workflow automatising the previously-run manual steps and run the HiggsToTauTau example on REANA.
Note: Computing efficiency
Note that the serial workflow will not be necessarily efficient here, since it will run sequentially over various dataset files and not process them in parallel. Do not pay attention to this inefficiency here yet. We shall speed up the serial example via parallel processing in the forthcoming HiggsToTauTau analysis: parallel episode coming after the coffee break.
Note: Container directories and workspace directories
The awesome-analysis-eventselection and awesome-analysis-statistics repositories assume that you
run code from certain absolute directories such as /analysis/skim. Recall that when REANA starts
a new workflow run, it creates a certain unique “workspace directory” and uses it as the default
directory for all the analysis steps throughout the workflow, allowing to share read/write files
amongst the steps.
It is a good practice to consider the absolute directories in your container images such as
/analysis/skim as read-only and rather use the dynamic workflow’s workspace for any writeable
needs. In this way, we don’t risk to write over any code or configuration files provided by the
container. This is good both for reproducibility and security purposes.
Moreover, we don’t modify the size of the running container by writing inside it, as it were. Writing to dynamic workspace that is mounted inside the container allows to keep the container size small.
Note: REANA_WORKSPACE environment variable
REANA platform uses a convenient set of environment variables that you can use in your scripts. One
of them is REANA_WORKSPACE which points to the workflow’s workspace which is uniquely allocated
for each run. You can use the $$REANA_WORKSPACE environment variable in your reana.yaml recipe
to share the output of skimming, histogramming, plotting and fitting steps. (Note the use of two
leading dollar signs to escape the workflow parameter expansion that you have used in the previous
episodes.)
OK, challenge time!
With the above hints in mind, please try to write workflow either individually or in pairs.
Exercise
Write
reana.yamlrepresenting HiggsToTauTau analysis and run it on the REANA cloud.
Solution
inputs: parameters: eosdir: root://eospublic.cern.ch//eos/root-eos/HiggsTauTauReduced workflow: type: serial specification: steps: - name: skimming environment: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3:master commands: - mkdir $$REANA_WORKSPACE/skimming && cd /analysis/skim && bash ./skim.sh ${eosdir} $$REANA_WORKSPACE/skimming - name: histogramming environment: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3:master commands: - mkdir $$REANA_WORKSPACE/histogramming && cd /analysis/skim && bash ./histograms_with_custom_output_location.sh $$REANA_WORKSPACE/skimming $$REANA_WORKSPACE/histogramming - name: plotting environment: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-eventselection-stage3:master commands: - mkdir $$REANA_WORKSPACE/plotting && cd /analysis/skim && bash ./plot.sh $$REANA_WORKSPACE/histogramming/histograms.root $$REANA_WORKSPACE/plotting 0.1 - name: fitting environment: gitlab-registry.cern.ch/awesome-workshop/awesome-analysis-statistics-stage3:master commands: - mkdir $$REANA_WORKSPACE/fitting && cd /fit && bash ./fit.sh $$REANA_WORKSPACE/histogramming/histograms.root $$REANA_WORKSPACE/fitting outputs: files: - fitting/fit.png
Key Points
Writing serial workflows is like chaining shell script commands