First example
Overview
Teaching: 15 min
Exercises: 5 minQuestions
How to run analyses on REANA cloud?
What are the basic REANA command-line client usage scenarios?
How to monitor my analysis using REANA web interface?
Objectives
Get hands-on experience with REANA command-line client
Overview
In this lesson we shall run our first simple REANA example. We shall see:
- structure of the example analysis and associated
reana.yamlfile - how to install of REANA command-line client
- how to connect REANA client to remote REANA cluster
- how to run analysis on remote REANA cluster
Checklist
Have you installed
reana-clientand/or have you logged into LXPLUS as described in Setup?
First REANA example
We shall get acquainted with REANA by means of running a sample analysis example:
Let’s start by cloning it:
git clone https://github.com/reanahub/reana-demo-root6-roofit
cd reana-demo-root6-roofit
What does the example do? The example emulates a typical particle physics analysis where the signal and background data is processed and fitted against a model. The example uses the RooFit package of the ROOT framework.
Four questions:
- Where is your input data? There is no input data. We shall simulate them.
- Where is your analysis code? Two files:
gendata.Cmacro generates signal and background data;fitdata.Cmacro makes a fit for the signal and the background data. - Which computing environment do you use? ROOT 6.18.04 with RooFit.
- What are the computational steps to achieve the results? Simple sequential steps: first run gendata, then run fitdata.
Workflow definition:
START
|
|
V
+-------------------------+
| (1) generate data |
| |
| $ root gendata.C ... |
+-------------------------+
|
| data.root
V
+-------------------------+
| (2) fit data |
| |
| $ root fitdata.C ... |
+-------------------------+
|
| plot.png
V
STOP
The four questions expressed in reana.yaml fully define our analysis:
inputs:
files:
- code/gendata.C
- code/fitdata.C
parameters:
events: 20000
data: results/data.root
plot: results/plot.png
workflow:
type: serial
specification:
steps:
- name: gendata
environment: 'docker.io/reanahub/reana-env-root6:6.18.04'
commands:
- mkdir -p results && root -b -q 'code/gendata.C(${events},"${data}")'
- name: fitdata
environment: 'docker.io/reanahub/reana-env-root6:6.18.04'
commands:
- root -b -q 'code/fitdata.C("${data}","${plot}")'
outputs:
files:
- results/plot.png
Note the basic structure of reana.yaml answering the Four Questions. (Where is input data? Where
is analysis code? What compute environment to use? What are the computational steps to arrive at
results?)
Exercise
Familiarise yourself with the RooFit demo example by studying the README file and looking at the
gendata.Candfitdata.Csource code.
Solution
firefox https://github.com/reanahub/reana-demo-root6-roofit
First steps with the REANA command-line client
First we need to make sure we can use REANA command-line client. See the setup instructions if you haven’t already installed it.
The client will offer several commands which we shall go through in this tutorial:
reana-client --help
Usage: reana-client [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
REANA client for interacting with REANA server.
Options:
-l, --loglevel [DEBUG|INFO|WARNING]
Sets log level
--help Show this message and exit.
Quota commands:
quota-show Show user quota.
Configuration commands:
info List cluster general information.
ping Check connection to REANA server.
version Show version.
Workflow management commands:
create Create a new workflow.
delete Delete a workflow.
diff Show diff between two workflows.
list List all workflows and sessions.
Workflow execution commands:
logs Get workflow logs.
restart Restart previously run workflow.
run Shortcut to create, upload, start a new workflow.
start Start previously created workflow.
status Get status of a workflow.
stop Stop a running workflow.
validate Validate workflow specification file.
Workspace interactive commands:
close Close an interactive session.
open Open an interactive session inside the workspace.
Workspace file management commands:
download Download workspace files.
du Get workspace disk usage.
ls List workspace files.
mv Move files within workspace.
prune Prune workspace files.
rm Delete files from workspace.
upload Upload files and directories to workspace.
Workspace file retention commands:
retention-rules-list List the retention rules for a workflow.
Secret management commands:
secrets-add Add secrets from literal string or from file.
secrets-delete Delete user secrets by name.
secrets-list List user secrets.
You can use --help option to learn more about any command, for example validate:
reana-client validate --help
Usage: reana-client validate [OPTIONS]
Validate workflow specification file.
The ``validate`` command allows to check syntax and validate the reana.yaml
workflow specification file.
Examples:
$ reana-client validate -f reana.yaml
Options:
-f, --file PATH REANA specification file describing the workflow to
execute. [default=reana.yaml]
--environments If set, check all runtime environments specified in
REANA specification file. [default=False]
--pull If set, try to pull remote environment image from
registry to perform validation locally. Requires
``--environments`` flag. [default=False]
--server-capabilities If set, check the server capabilities such as
workspace validation. [default=False]
-t, --access-token TEXT Access token of the current user.
--help Show this message and exit.
Exercise
Validate our
reana.yamlfile to discover any errors. Usevalidatecommand to do so.
Solution
reana-client validate==> Verifying REANA specification file... reana.yaml -> SUCCESS: Valid REANA specification file. ==> Verifying REANA specification parameters... -> SUCCESS: REANA specification parameters appear valid. ==> Verifying workflow parameters and commands... -> SUCCESS: Workflow parameters and commands appear valid. ==> Verifying dangerous workflow operations... -> SUCCESS: Workflow operations appear valid.
Connect REANA client to remote REANA cluster
The REANA client will interact with a remote REANA cluster. It knows to which REANA cluster it connects by means of the following environment variable:
export REANA_SERVER_URL=https://reana.cern.ch
In order to authenticate to REANA, you need to generate a token.
Exercise: Obtain a token.
In order to obtain your token, please go to https://reana.cern.ch and ask for it.
In your terminal, paste the line with your new access token as seen below.
export REANA_ACCESS_TOKEN=xxxxxx
It may be a good idea to create a reana-setup-environment.sh file to store these two export
commands. That way you all you need to do to setup your environment is source
reana-setup-environment.sh. An alternative to this is opening up your .bashrc file and pasting
the above two export commands there.
The REANA client connection to remote REANA cluster can be verified via ping command:
reana-client ping
REANA server: https://reana.cern.ch
REANA server version: 0.9.1
REANA client version: 0.9.1
Authenticated as: John Doe <john.doe@example.org>
Status: Connected
Run example on REANA cluster
Now that we have defined and validated our reana.yaml, and connected to the REANA production
cluster, we can run the example easily via:
reana-client run -w roofit
==> Creating a workflow...
==> Verifying REANA specification file... reana.yaml
-> SUCCESS: Valid REANA specification file.
==> Verifying REANA specification parameters...
-> SUCCESS: REANA specification parameters appear valid.
==> Verifying workflow parameters and commands...
-> SUCCESS: Workflow parameters and commands appear valid.
==> Verifying dangerous workflow operations...
-> SUCCESS: Workflow operations appear valid.
==> Verifying compute backends in REANA specification file...
-> SUCCESS: Workflow compute backends appear to be valid.
roofit.1
==> SUCCESS: File /reana.yaml was successfully uploaded.
==> Uploading files...
==> Detected .gitignore file. Some files might get ignored.
==> SUCCESS: File /code/gendata.C was successfully uploaded.
==> SUCCESS: File /code/fitdata.C was successfully uploaded.
==> Starting workflow...
==> SUCCESS: roofit.1 is pending
Here, we use run command that will create a new workflow named roofit, upload its inputs as
specified in the workflow specification and finally start the workflow.
While the workflow is running, we can enquire about its status:
reana-client status -w roofit
NAME RUN_NUMBER CREATED STARTED STATUS PROGRESS
roofit 1 2020-02-17T16:01:45 2020-02-17T16:01:48 running 1/2
After a minute or so, the workflow should finish:
reana-client status -w roofit
NAME RUN_NUMBER CREATED STARTED ENDED STATUS PROGRESS
roofit 1 2020-02-17T16:01:45 2020-02-17T16:01:48 2020-02-17T16:02:44 finished 2/2
We can list the output files in the remote workspace:
reana-client ls -w roofit
NAME SIZE LAST-MODIFIED
reana.yaml 687 2020-02-17T16:01:46
code/gendata.C 1937 2020-02-17T16:01:46
code/fitdata.C 1648 2020-02-17T16:01:47
results/plot.png 15450 2020-02-17T16:02:44
results/data.root 154457 2020-02-17T16:02:17
We can also inspect the logs:
reana-client logs -w roofit | less
# (Hit q to quit 'less')
==> Workflow engine logs
2020-02-17 16:02:10,859 | root | MainThread | INFO | Publishing step:0, cmd: mkdir -p results && root -b -q 'code/gendata.C(20000,"results/data.root")', total steps 2 to MQ
2020-02-17 16:02:23,002 | root | MainThread | INFO | Publishing step:1, cmd: root -b -q 'code/fitdata.C("results/data.root","results/plot.png")', total steps 2 to MQ
2020-02-17 16:02:50,093 | root | MainThread | INFO | Workflow 424bc949-b809-4782-ba96-bc8cfa3e1a89 finished. Files available at /var/reana/users/b57e902f-fd11-4681-8a94-4318ae05d2ca/workflows/424bc949-b809-4782-ba96-bc8cfa3e1a89.
==> Job logs
==> Step: gendata
==> Workflow ID: 424bc949-b809-4782-ba96-bc8cfa3e1a89
==> Compute backend: Kubernetes
==> Job ID: 53c97429-25e9-4b74-94f7-c665d93fdbc2
==> Docker image: reanahub/reana-env-root6:6.18.04
==> Command: mkdir -p results && root -b -q 'code/gendata.C(20000,"results/data.root")'
==> Status: finished
==> Logs:
...
We can download the resulting plot:
reana-client download results/plot.png -w roofit
==> SUCCESS: File results/plot.png downloaded to reana-demo-root6-roofit.
And display it:
firefox results/plot.png
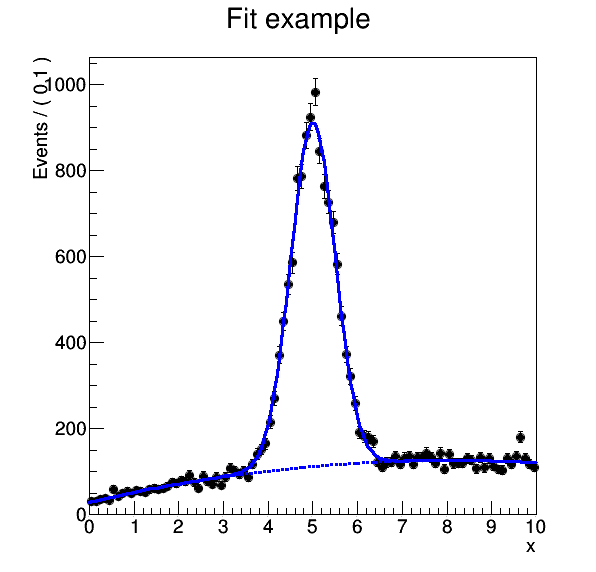
Exercise
Run the example workflow on REANA cluster. Practice
status,ls,logs,downloadcommands. For example, can you get the logs of the gendata step only?
Solution
reana-client logs -w roofit --filter step=gendata
Key Points
Use
reana-clientrich command-line client to run containerised workflows from your laptop on remote compute cloudsBefore running analysis remotely, check locally its correctness via
validatecommandAs always, when it doubt, use the
--helpcommand-line argument