All the World's a Stage
Overview
Teaching: 5 min
Exercises: 5 minQuestions
How do you make some jobs run after other jobs?
Objectives
Make multiple stages and run some jobs in serial.
Defining Stages
From the last session, we’re starting with
hello_world:
script:
- echo "Hello World"
.template_build:
before_script:
- COMPILER=$(root-config --cxx)
- FLAGS=$(root-config --cflags --libs)
script:
- $COMPILER -g -O3 -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic -o skim skim.cxx $FLAGS
multi_build:
extends: .template_build
image: $ROOT_IMAGE
parallel:
matrix:
- ROOT_IMAGE: ["rootproject/root:6.28.10-ubuntu22.04","rootproject/root:latest"]
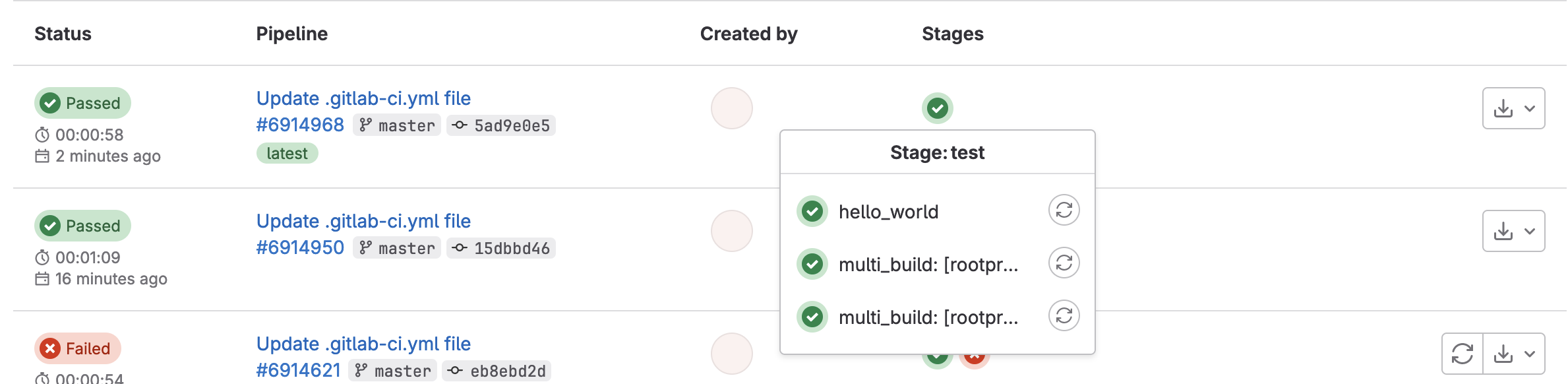
We’re going to talk about another global parameter :stages (and the associated per-job parameter :job:stage. Stages allow us to group up parallel jobs with each group running after the other in the order you define. What have our jobs looked like so far in the pipelines we’ve been running?
Default Stage
You’ll note that the default stage is
test. Of course, for CI/CD, this is likely the most obvious choice.
Stages allow us to categorize jobs by functionality, such as build, or test, or deploy – with job names being the next level of specification such as test_cpp, build_current, build_latest, or deploy_pages. Remember that two jobs cannot have the same name (globally), no matter what stage they’re in. Like the other global parameter variables, we keep stages towards the top of our .gitlab-ci.yml file.
Adding Stages
Let’s add stages to your code. We will define two stages for now:
greetingandbuild. Don’t forget to assign those stages to the appropriate jobs.Solution
stages: - greeting - build hello world: stage: greeting script: - echo "Hello World" .template_build: stage: build before_script: - COMPILER=$(root-config --cxx) - FLAGS=$(root-config --cflags --libs) script: - $COMPILER -g -O3 -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic -o skim skim.cxx $FLAGS multi_build: extends: .template_build image: $ROOT_IMAGE parallel: matrix: - ROOT_IMAGE: ["rootproject/root:6.28.10-ubuntu22.04","rootproject/root:latest"]
If you do it correctly, you should see a pipeline graph with two stages
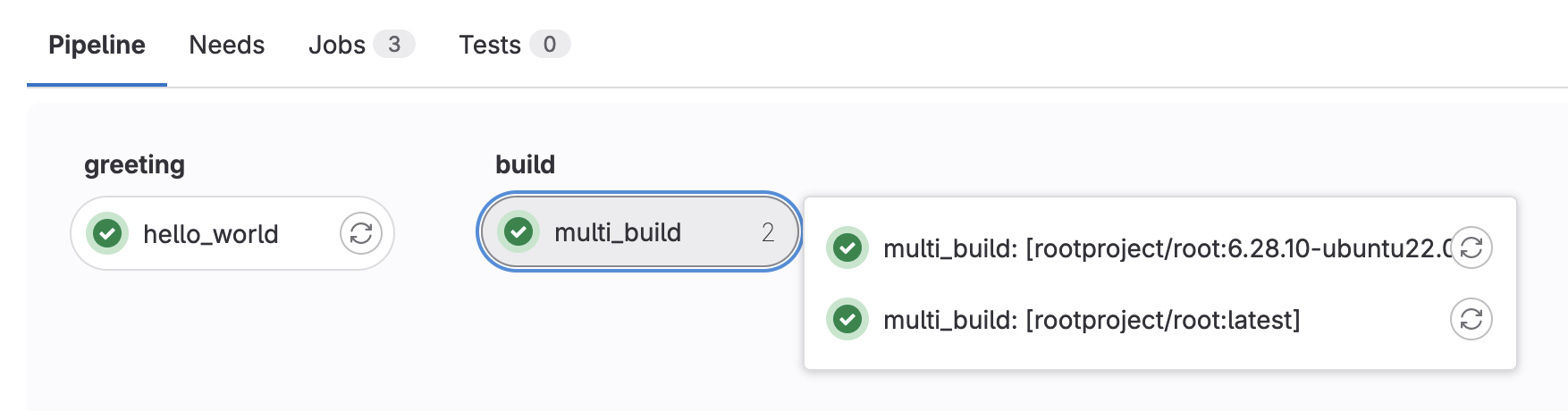
Now all jobs in greeting run first, before all jobs in build (as this is the order we’ve defined our stages). All jobs within a given stage run in parallel as well.
That’s it. There’s nothing more to stages apart from that! In fact, everything in terms of parallel/serial as well as job dependencies only make sense in the context of having multiple stages. In all the previous sessions, you’ve just been using the default test stage for all jobs; the jobs all ran in parallel.
Further Reading
Key Points
Stages allow for a mix of parallel/serial execution.
Stages help define job dependencies.