Set up Python
Part of this lesson consists in learning how to make scripts exit correctly. At some point, we will need to test exit codes with Pytest, Python testing tool.
To know whether your Python has pytest, just run python -c "import pytest". If this command returns nothing, it means everything is fine. Otherwise, it can be installed by running python -m pip install -U pytest. More information can be found in the pytest website for installation.
Set up the code
-
Create a new project on your personal GitHub account and name it
virtual-pipelines-eventselection.Make sure you click Public for the visibility level of the new project so that everyone can see your awesome work.
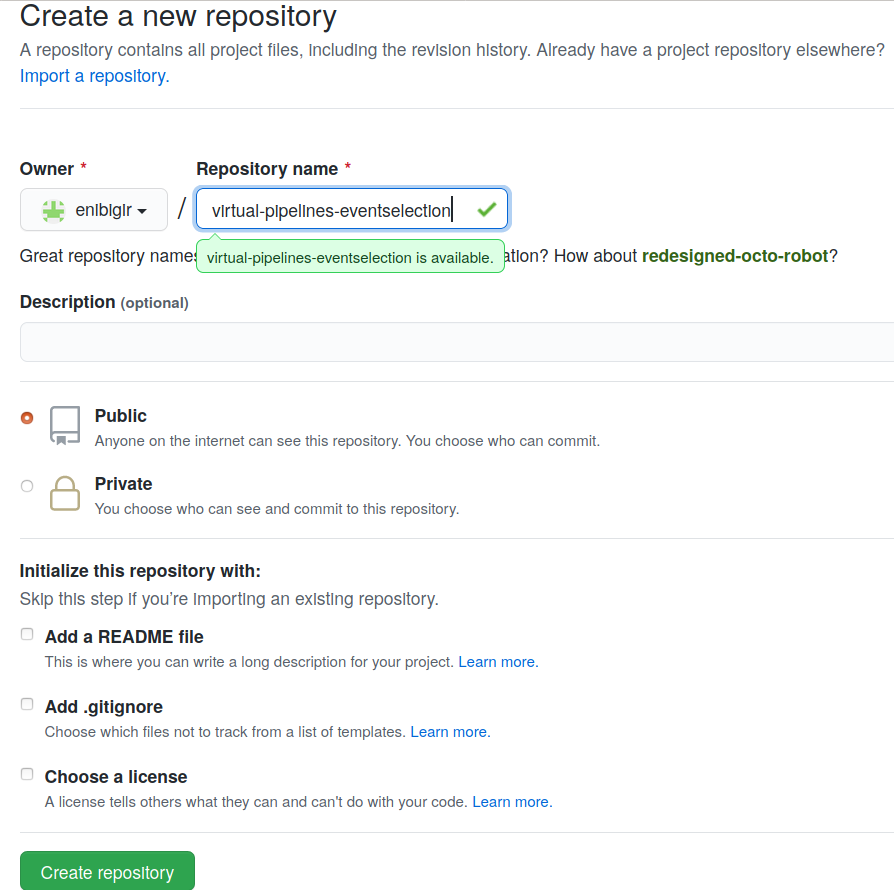
-
Get the code
Open a terminal and clone the repository that contains files required for this lesson.
git clone git@github.com:hsf-training/hsf-training-cms-analysis.git virtual-pipelines-eventselection cd virtual-pipelines-eventselection -
Add the code to your personal GitHub account
At the moment, your clone is the remote repository stored on someone GitHub account. To get the name of the existing remote use
git remote -v # -v stands for verboseorigin git@github.com:hsf-training/hsf-training-cms-analysis.git (fetch) origin git@github.com:hsf-training/hsf-training-cms-analysis.git (push)You have to change remote’s URL in order to be able to add the code to your personal GitHub account.
git remote set-url origin git@github.com:<GitHub username>/virtual-pipelines-eventselection.gitCheck again the name of the current remote:
git remote -vThe last step is to rename the branch to main, and push it to GitHub.
git branch -M main git push -u origin mainThis will add the code to your new repository on GitHub. Done!
If you’re having issues, please let us know immediately since you might not be able to follow this lesson without a proper setup.